Monitoring the Yeast in Fermentation for Sugar Wash

Disclaimer: This post might include affiliate links, through which I may earn a small commission without any extra cost to you. Additionally, I am an Amazon Associate and earn from eligible purchases. All the products and services I suggest are ones I have personally used or would use. Thank you very much for your support if you decide to buy through any of my links!
Come join the Distilling Squad!
Get the best fundamental tips & tricks here. Woohoo!
Yeast in fermentation plays a BIG role, the yeast cells convert sugars (glucose) into alcohol and carbon dioxide (ethanol).
This process is used for distilling, brewing and winemaking, and requires careful monitoring and management of yeast to ensure great results. Yeast is used in multiple items from bread dough, to beer and wine.
Here are key stages and considerations for monitoring yeast in fermentation for your sugar wash batch specifically.
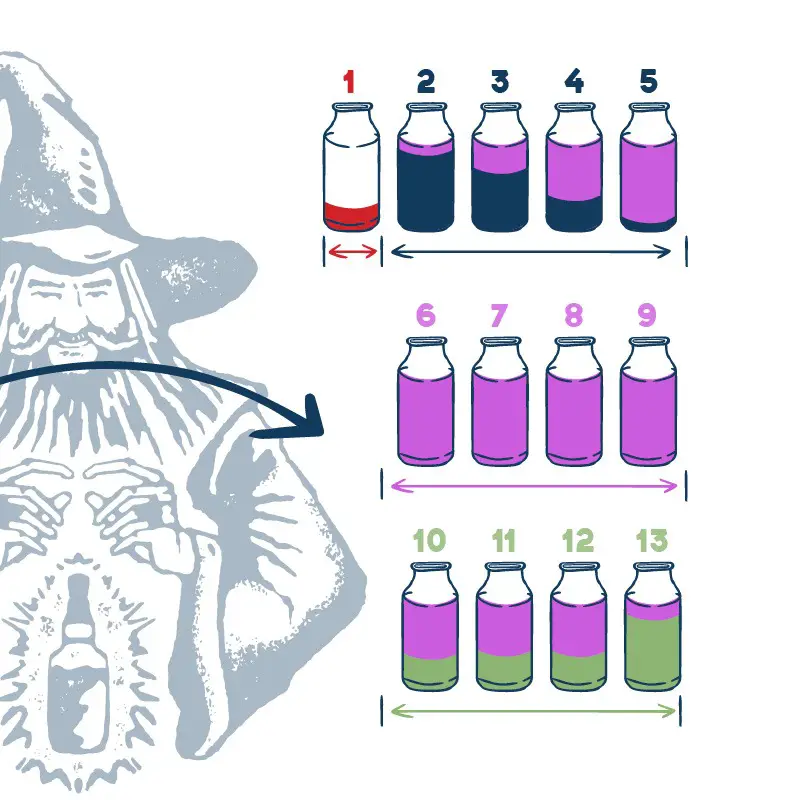
Key Stages in Monitoring Yeast in Fermentation
Your first thing is to understand the yeast strain being used in your sugar wash. The yeast species is a microorganism and grows with temperature and nutrients.
1. Recognising the Exothermic Reaction
2. pH Level Adjustment in the ferment
3. CO2 Monitoring
4. Final Gravity (FG) Check
5. Calculating Potential Alcohol in the process of fermentation
6. Documentation of the type of fermentation is important
What you need to know about the yeast fermentation process
Understand the role of yeast in fermentation
By closely monitoring the exothermic reaction, adjusting pH levels, observing CO2 output, and verifying fermentation is completed.
It is done through SG checks, the distillers can optimise yeast performance and alcohol yield. You know, each batch of fermentation is an opportunity to learn and improve, making documentation a key component of success.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a hobbyist, mastering these aspects of yeast in fermentation will enhance the quality and consistency of your fermented products.
Last Updated on Feb 08, 2024 by The Brew Mechanic
Disclosure: I may receive affiliate compensation for some of the links below at no cost to you if you decide to purchase a product or service. You can read our affiliate disclosure in our privacy policy. The information provided is for entertainment only.

With 35 years of knowledge of being a chemical engineer in alcohol manufacturing plants, my mission is to teach the next generation of home distilling alcohol brewers at a supernatural speed.
My reviews are based on real-life experiences with reflux stills, sugar wash, troubleshooting and mystical chemical reactions.